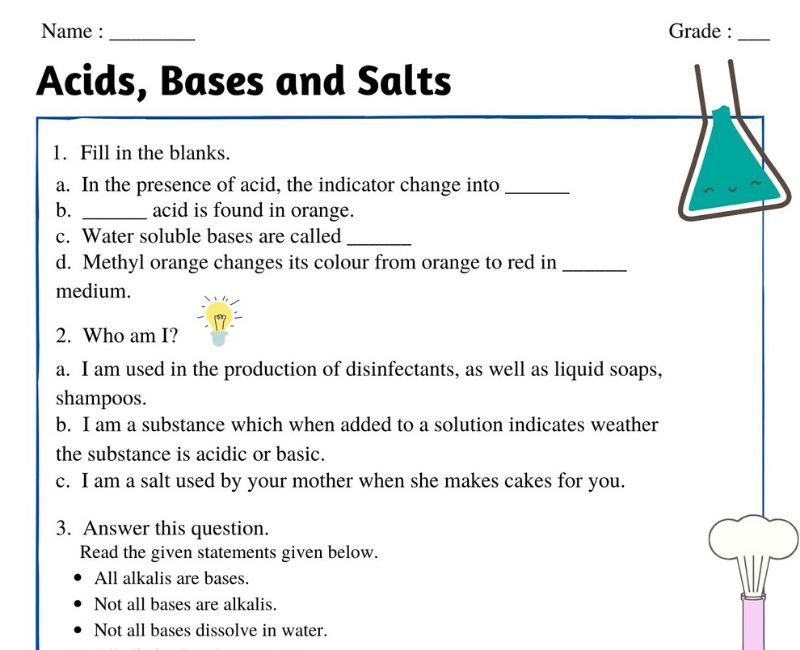
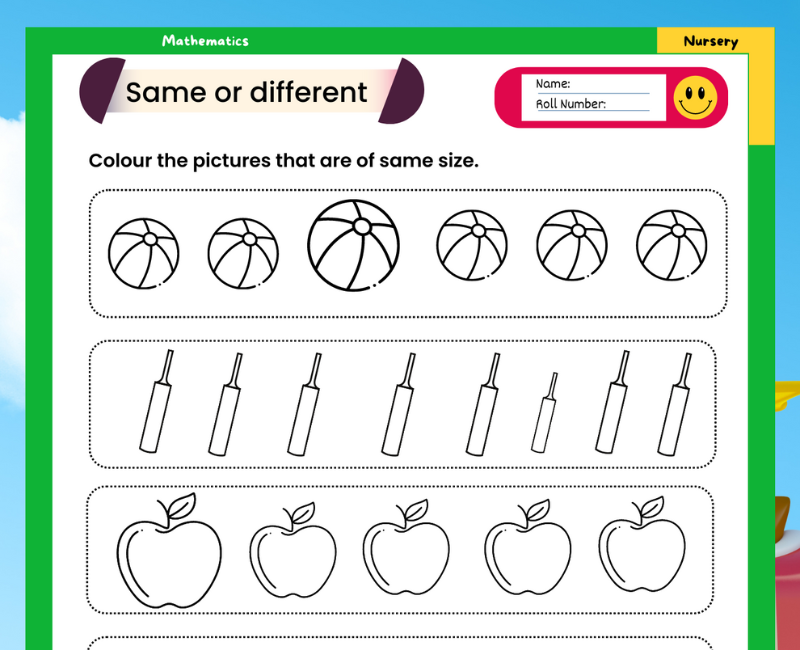
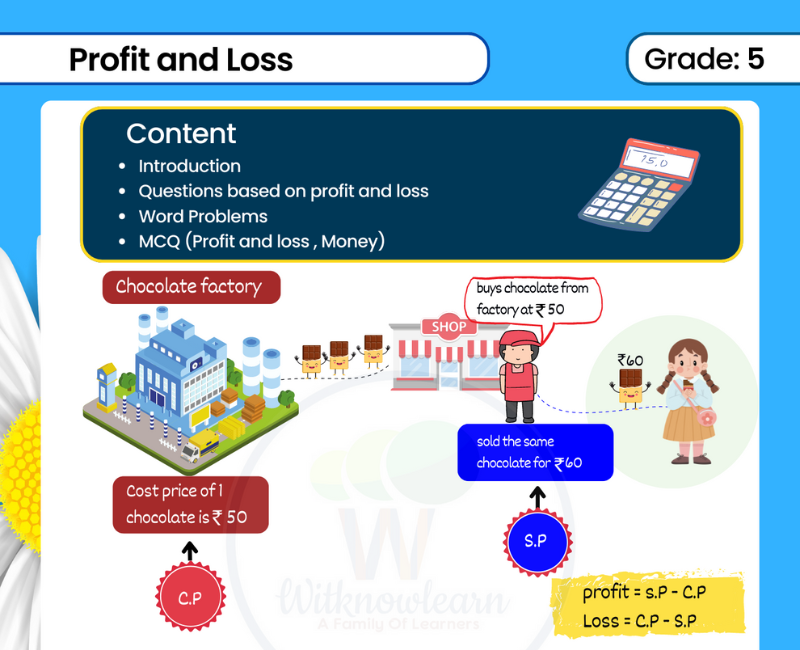
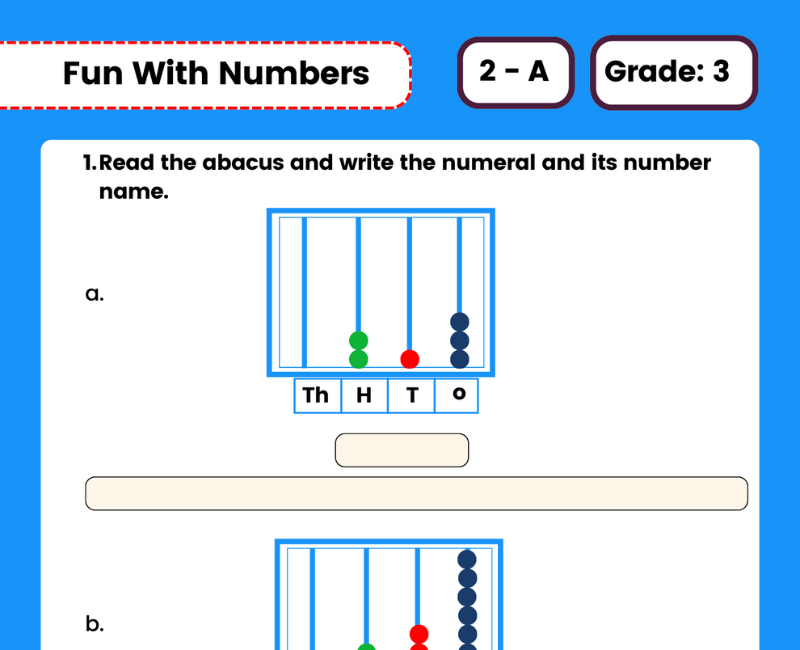
Acids Bases And Salts Class 7 Worksheet
Dive into the bubbling world of Acids, Bases, and Salts with the Class 7 Worksheet that’s all set to zest up your learning like a slice of lemon in a soda! Ever wondered why that lemon tart tastes so tangy or why soap feels slippery? Class 7 Acids, Bases, and Salts are the mysterious characters behind these everyday sensations, and this worksheet is your golden ticket to unraveling their secrets.
As you step into the lab of Class 7 science chapter 4, be prepared for exciting reactions. Every page of the Class 7 science chapter 4 worksheet is a new adventure waiting to fizz up. You won't just read about what acids and bases are; you'll test their presence like a true scientist. Imagine being able to tell if something is an acid or a base just by looking at the results of your simple yet thrilling experiments within the classroom or at home.
Now, who doesn't love a good challenge? Flex your brain muscles with the Acids Bases And Salts Class 7 extra questions that add a pinch of extra flavor to your study recipe. These aren't just plain question and answers — they're puzzles that tickle your mind, making you think harder and smarter.
Get ready to be fascinated by how acids react with metals and how bases can turn certain vegetables into wild new colors. And when we say this chapter is important, we mean it could pop up anywhere, from your food to the soap in your bathroom!
The class 7 science chapter 5 acids bases and salts notes will be like your trusty sidekick in this adventure, offering you hints, tips, and all the key points you'll need to remember. These notes aren't just a summary — they're your cheat sheet to acing the tests and impressing everyone with your acid-base superpowers.
So, are you ready to soak up all the amazing facts like a sponge? Grab your Acids Bases And Salts Class 7 Worksheet and let's start this electrifying educational journey. You're just one worksheet away from becoming an acid-base wizard, transforming the mundane into the magical through the science of reactions!